Can Urban Digital Twins Support the Realization of Sustainable Development Goal 11? Identifying Key Social and Technical Challenges
Abstract
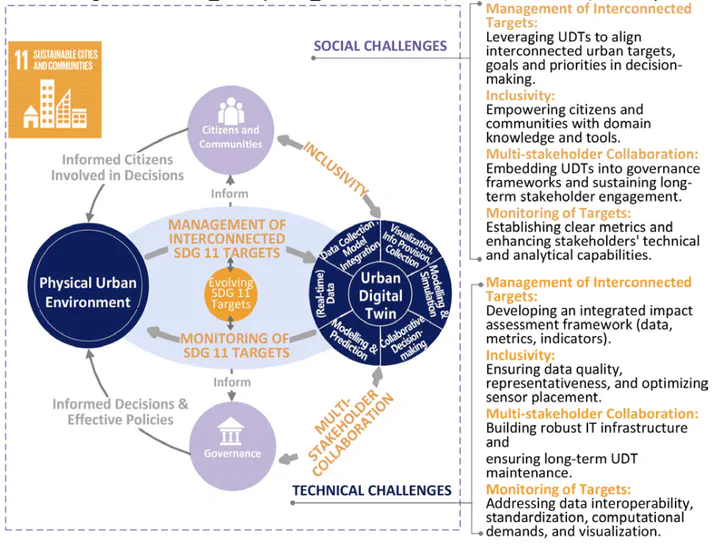
The rapid urbanization of cities presents significant sustainability challenges, necessitating big data and digital tools as solutions for efficient resource management. A key advancement in this area is the Urban Digital Twin (UDT). UDTs aim to create dynamic virtual replicas of urban environments, enabling informed decision-making for city planners and policymakers. UDTs enable predictive modeling, resource optimization, and impact assessment of urban interventions. On the other hand, one of the globally accepted sustainable development goals (SDGs) to achieve by 2030 is SDG 11, which focuses specifically on “Sustainable Cities and Communities”. SDGs and SDG 11 consider the cities as a system that consists of the physical urban environment and social dynamics coming from governance, citizens and communities. However, current research on UDTs has primarily focused on technical aspects, leaving the potential of UDTs to support SDG 11 and its social dynamics underexplored. This study aims to understand whether UDTs can support the realization of SDG 11. Therefore, we explore how the capabilities of UDTs, such as monitoring, modelling and simulation, visualization, information provision and collection can support the SDG 11 principles of managing interconnected targets, inclusivity, multi-stakeholder collaboration, and monitoring of SDG 11 targets. We propose a socio-technical framework illustrating how UDTs can support SDG 11 and outline the key social and technical challenges to be addressed to fully realize UDTs’ potential. Finally, we discuss the conclusions and outlook for overcoming such challenges.