Abstract
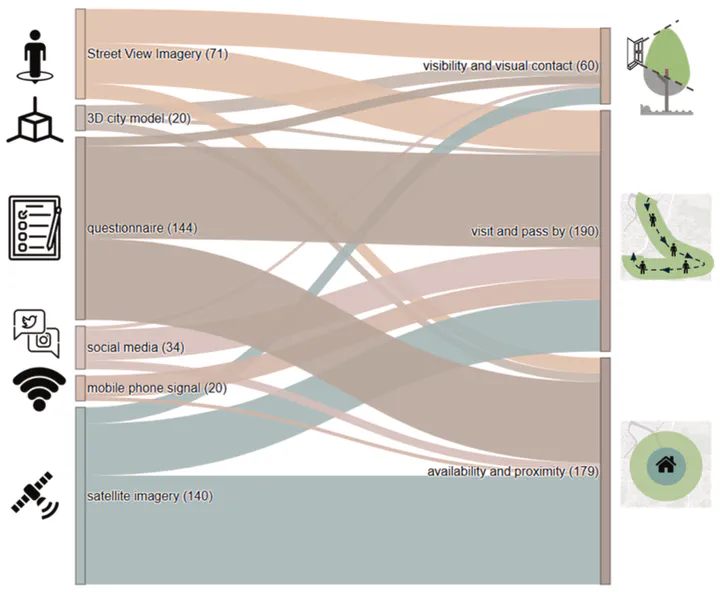
Greenery plays a vital role in urban environments, providing numerous benefits through diverse pathways. Various metrics and methodologies have been proposed to assess multiple dimensions of greenery exposure. For a comprehensive and precise assessment of greenery exposure for different research purposes, it is crucial to identify the most suitable methods and data sources. However, existing reviews primarily address the health outcomes of urban greenery, rather than the methods of assessing greenery exposure. To address this gap, we conducted a review of 312 research articles, focusing on methodologies and technologies for measuring greenery exposure in urban settings. This review categorizes exposure measurement techniques into three categories: proximity-based, mobility-based, and visibility-based, evaluating their strengths, limitations, and synergies. Proximity-based methods generally assess overall greenery level in residential areas or other locations, but they fall short in capturing the actual interactions between humans and greenery. Mobility-based methods track real-time human location and assess greenery exposure based on travel trajectories, but they neglect the specific nature of human-greenery interactions. In contrast, emerging visibility-based methods offer opportunities to measure potential visual interactions between individuals and greenery. We found emerging metrics tend to integrate 3D data, qualitative aspects, and diverse data sources. We advocate for an integrated approach that encompasses both human mobility and potential interactions with greenery across various areas. We also argue that data granularity is balanced against cost, scalability, and ethical constraints. Our comprehensive review offers a framework and categorization to guide studies in designing exposure measurements aligned with their research objectives.